The seemingly indefatigable U.S. consumer is finally starting to tire out. Retail sales fell 1.1% in December. Not only was the drop sharper than expected, but it came on top of downward revisions to November sales. Some pullback in retail spending seemed inevitable after sales had surged more than 30% above early 2020 levels and the pandemic-induced shift to goods in lieu of services unwound. Yet, the details of the report suggest the decline is more troubling than retail merely hitting an air pocket after demand for many items was pulled forward. Instead, the report hinted that consumers are retrenching more broadly. Grocery store sales were flat over the month despite higher food prices, while receipts at restaurants and bars were down 1.3% in real terms by our estimates in a sign consumers are cutting back on discretionary services in addition to goods. Control group sales, which feed into the BEA's calculation of GDP, declined 0.7% in December, the steepest drop in more than a year. Along with downward revisions to the two prior months, we have downwardly revised our estimate for Q4 consumer spending to an annualized rate of 2.7% from 3.4%.
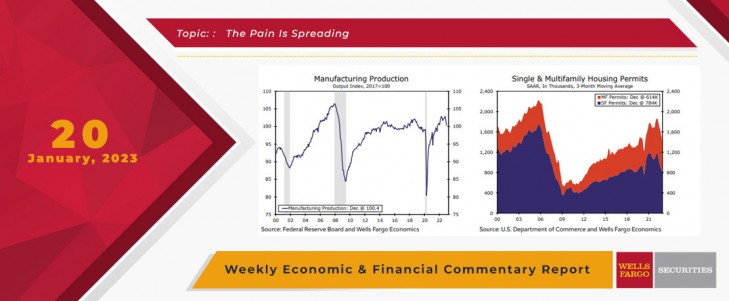
Fading demand for goods has also started to take an undeniable toll on manufacturing. Manufacturing output plummeted 1.3% in December, and similar to retail sales, previous estimates of production were revised lower. Output of consumer durables and non-energy durables fell over the month, but the pain of higher interest rates and concerns about recession are spreading, with business equipment declining 2.0%. A survey of the manufacturing sector released this week pointed to further deterioration ahead. The Empire Manufacturing and Philly Fed indices both remained in contractionary territory in January, with new orders again falling according to each survey.
While retail and manufacturing have only recently started to falter in the face of higher interest rates and increasingly stretched consumers, the housing market has been overwhelmed by these headwinds for a year now. Data this week showed that the sharpest leg of the sector's adjustment may be behind us, but residential real estate remains under severe pressure. Building permits continued to slide in December, led by a 6.5% drop for single-family units. Meanwhile, a rise in permits in the lumpier multifamily segment only partially reversed the prior months' declines. Multifamily permits are now down 27% over the past year, only marginally less depressed than the 39% decline in single-family permits. Sales of existing homes also continued to decline in December and ended the year at their slowest pace since 2010.
That said, a pullback in mortgage rates as the end of the Fed's tightening cycle comes into view is helping to breathe at least a little more life into housing demand. Purchase applications jumped 25% the week end Jan. 13, and mortgage rates have continued to slide with the 30-year fixed rate dipping to 6.15%, the lowest reading since September. Lower financing costs alongside some relief in material prices the past couple of months helped builder sentiment tick up for the first time in 13 months in January. A sustained improvement, however, is likely some ways off, as weaker household finances and still-elevated mortgage rates keep the environment for builders challenging.
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 08 May 2020
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / May 15, 2020
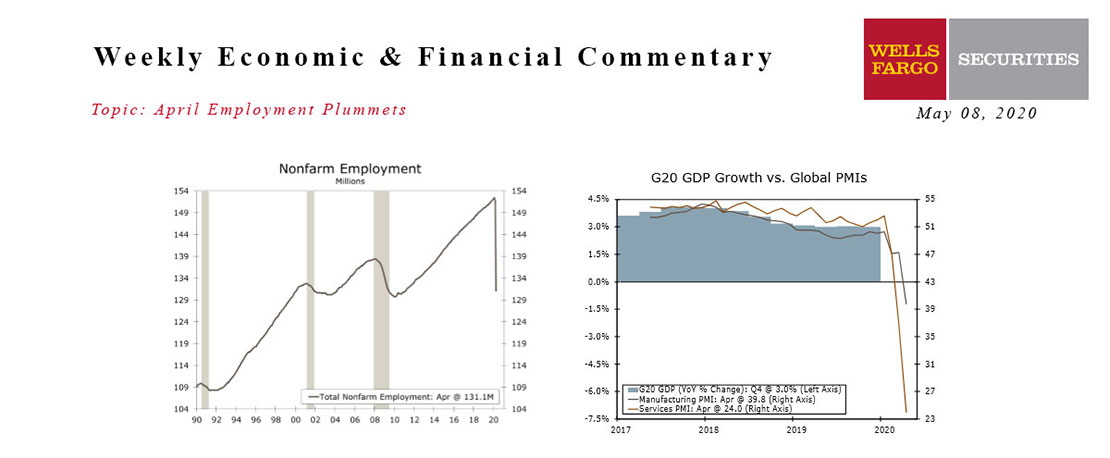
April nonfarm payrolls confirmed what we already knew—the labor market is collapsing. By the survey week of April 12, net employment had fallen by 20,500,000 jobs.
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 05 August 2022
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Aug 08, 2022
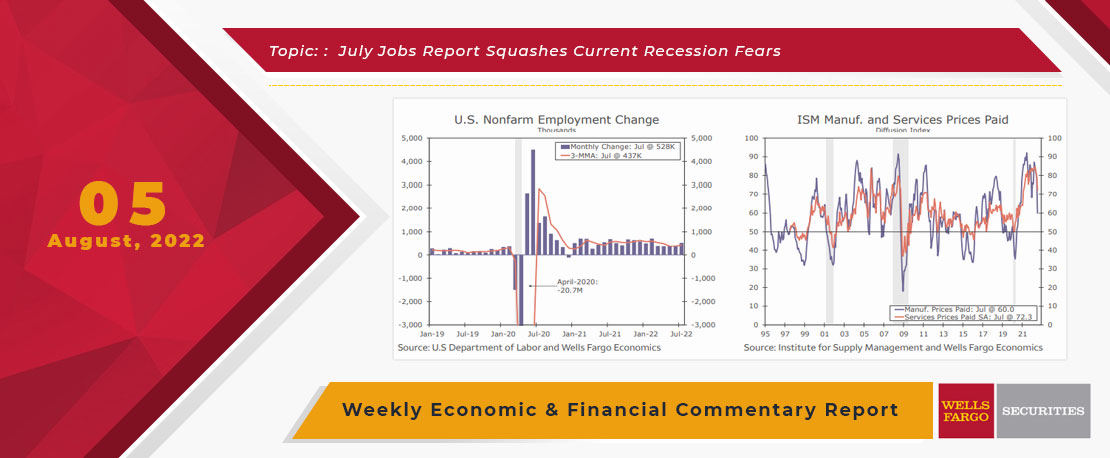
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported this morning that nonfarm payrolls increased 528,000 for the month of July, easily topping estimates, lowering the unemployment rate to 3.5%.
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 20 August 2021
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Aug 24, 2021
The Wells Fargo Economics team notes in the Commentary that new COVID cases in New Zealand disrupted the Reserve Bank of New Zealand\'s plan to tighten monetary policy this week.
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 24 April 2020
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Apr 27, 2020
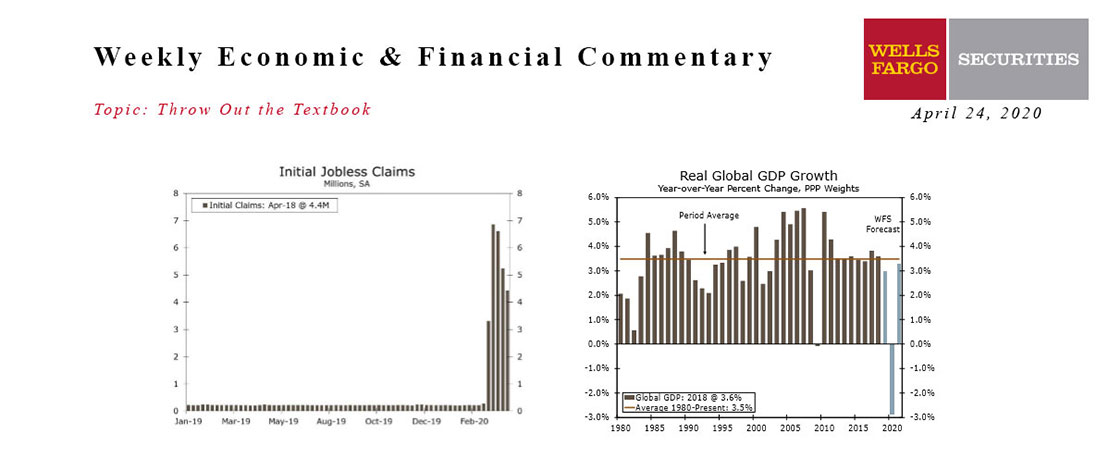
Oil prices went negative for the first time in history on Monday as the evaporation of demand collided with a supply glut. In the past five weeks, 26.5 million people have filed for unemployment insurance, or more than one out of every seven workers.
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 17 September 2021
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Sep 23, 2021
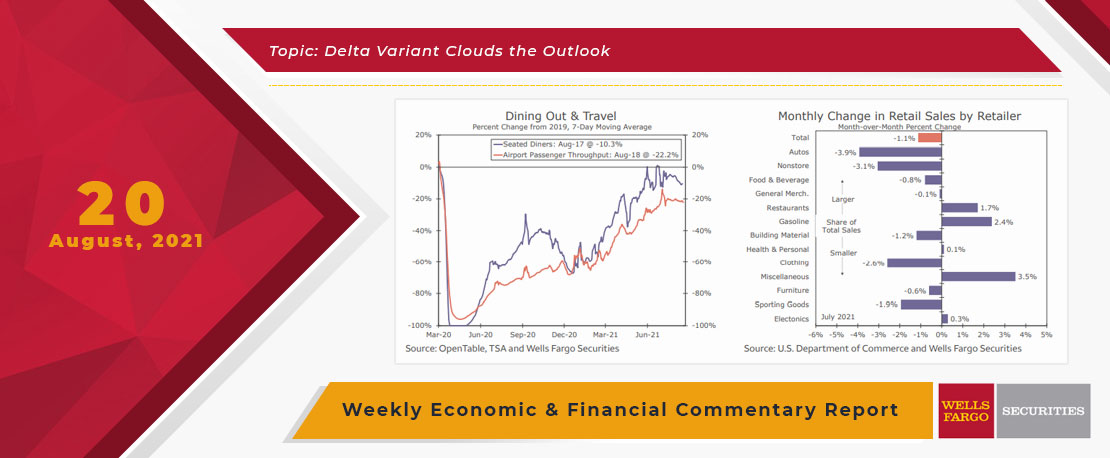
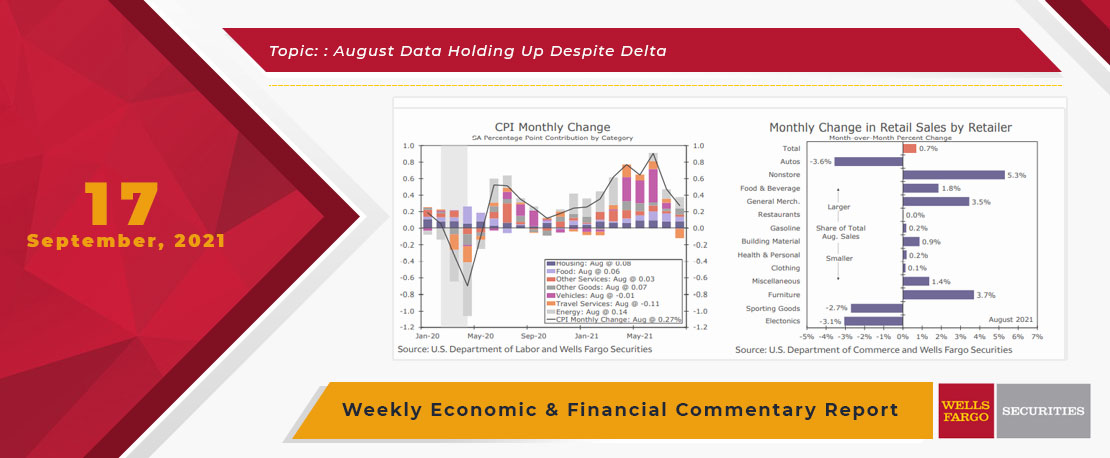
While we were picking up tree limbs from the yard, data released this week generally showed a stronger economy in August than many expected in the wake of surging COVID cases.
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 18 September 2020
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Sep 15, 2020
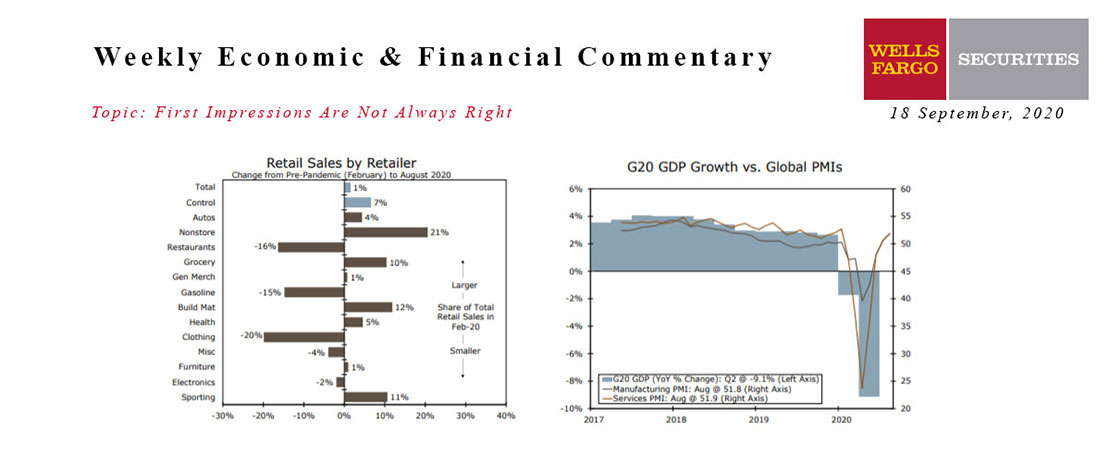
The details were generally more favorable. The retail sectors hurt most by the pandemic saw gains in August, factory output is growing and soaring homebuilder confidence suggests soft construction data this week may be transitory.
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 25 September 2020
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Sep 28, 2020
Existing home sales rose 2.4% to a 6.0-million unit annual pace. The surge in sales further depleted inventories and pushed prices sharply higher.
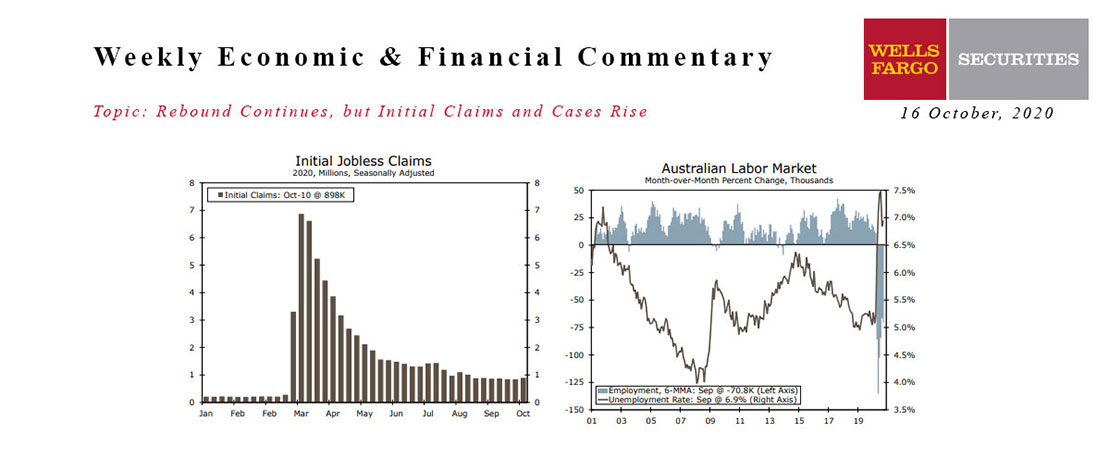
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 16 October 2020
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Oct 20, 2020
Data continue to reflect an economy digging itself out of the lockdown-induced slump.
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 09 April 2020
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Apr 10, 2020
The Federal Reserve announced a series of measures this morning that are intended to assist households, businesses and state & local governments as they cope with the economic fallout of the COVID-19 outbreak.
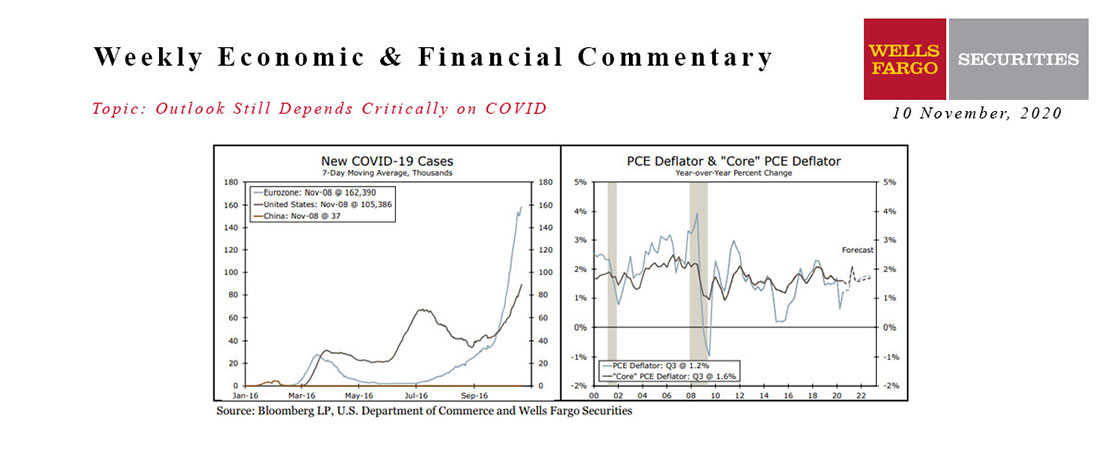
This Week's State Of The Economy - What Is Ahead? - 10 November 2020
Wells Fargo Economics & Financial Report / Nov 17, 2020
The U.S. election has come and gone, but we have not made any meaningful changes to our economic outlook, which continues to look for further expansion in the U.S. economy in coming quarters.